
研究レビュー 2006年度
(1) 新しい顕微振動分光法「顕微ハイパーラマン分光法」の開発
線形および非線形顕微ラマン分光法は、不均一な分子系のin situ または in vivo 解析の有力な手段として広く用いられている。顕微ラマン分光法では、共焦点光学配置を採用することにより、サブマイクロメートルの空間分解能を容易に達成することができる。一方、顕微ラマン分光と相補的である顕微赤外分光の空間分解能は、光の回折限界による制限のために、5—10 μmに止まる。我々はハイパーラマン散乱を用いて、顕微赤外分光と同等な新しい顕微振動分光法を開発した。ハイパーラマン散乱は、ラマン散乱や赤外線吸収と異なる選択律を持つ。赤外活性な振動はすべてハイパーラマン活性であり、赤外/ラマン同時不活性な振動もハイパーラマン活性な場合がある。図1は赤外活性、ラマン不活性なC=C伸縮バンド(1564 cm-1)を用いて得たβ-carotene微結晶のハイパーラマンイメージである。励起波長は800 nmで横方向の空間分解能は0.6 μm、奥行き方向の空間分解能は1.4 μmである。このように、我々はハイパーラマン散乱を用いることによって、可視顕微分光の高い空間分解能を保ちつつ、赤外活性振動を観測することができるようになった。
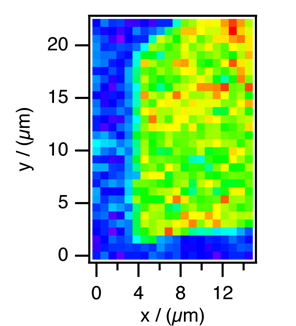
図1.β-carotene微結晶のハイパーラマンイメージ.
(2) 電場変調赤外分光によるCH3CN/CCl4混合溶媒中のp-ニトロアニリンの溶媒和構造
我々は先に、CH3CN/CCl4混合溶媒中のp-ニトロアニリンが、CH3CN 分子1個(1:1 型)および2個(1:2型)と強く相互作用した溶媒和構造を作ることを報告した。電場変調赤外分光は、外部から印加された電場による配向分極や電子分極に起因する赤外線吸収の微小変化を検出する。配向分極信号は溶質分子の電気双極子モーメントに関する定量的情報を含み、電子分極信号は分極率に関する情報を含む。これら2種の信号は、印加電場と入射赤外光の電場のなす角?に対する依存性が異なるので、実験的に分離することができる。CH3CN/CCl4 中のp-ニトロアニリンの電場変調赤外吸収スペクトルのχ依存性を図2に示す。このχ依存性を特異値解析し、ab initio計算 (HF/6-31+G** level)と組み合わせることにより、図3に示すような溶媒和構造を得ることができた。
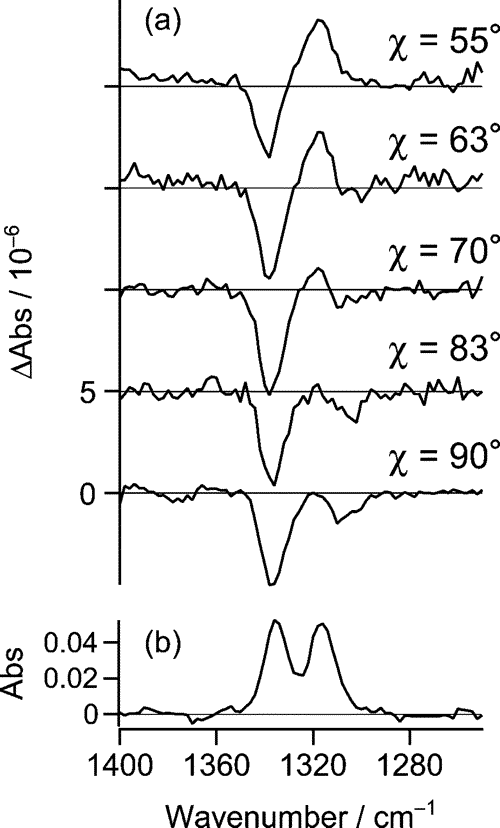
図2 The observed χdependence of electroabsorption of pNA in CH3CN/CCl4 mixed solvent.
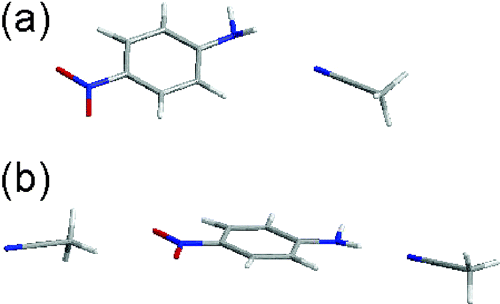
図3 The structure of the 1:1 form (a) and that of 1:2 form (b).
原著論文
- Raman spectra indicative of unusual water structure in crystals formed from a room-temperature ionic liquid. Hiroko Miki, Satoshi Hayashi, Hiroshige Kikura and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, J. Raman Spectrosc., 37, 1242-1243 (2006).
- Vibrational imaging of a J-aggregate microcrystal using ultrabroadband multiplex coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microspectroscopy. Hideaki Kano and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, Vibrational Spectrosc., 42 (1) 135-139 (2006).
- Magnetic manipulation of materials in a magnetic ionic liquid. Masanari Okuno, Satoshi Hayashi and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, Appl. Phys. Lett., 89, 132506 (2006).
- Evidence for mesoscopic local structures in ionic liquids: CARS signel spatial distribution of C(n)mim[PF6] (n=4,6,8). Shinsuke Shigeto and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, Chem. Phys. Lett., 427, 329-332 (2006).
- Ion association dynamics in aqueous solutions of sulfate salts as studied by Raman band shape analysis. DaisukeWatanabe and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, J. Chem. Phys., 124, 247102 (2006).
- Heat capacity and glass transition of an ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Osamu Yamamuro, Y.Minamimoto, Y. Inamura, Satoshi Hayashi and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, Chem. Phys. Lett., 423, 371-375 (2006).
- Vibrationally resonant imaging of a single living cell by supercontinuum-based multiplex coherent anti-Stokes Raman Scattering microspectroscopy. Hideaki Kano and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, Optics Express 13, 1322-1327 (2005).
- In-vivo multi-nonlinear optical imaging of a living cell using a supercontinuum light source generated from a photonic crystal fiber. Hideaki Kano and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, Optics Express 14, 2798-2804 (2006).
- Structure and dipole moments of the two distinct solvated forms of p-nitroaniline in acetonitrile/CCl4 as studied by infrared electroabsorption spectroscopy. Shinsuke Shigeto, Hirotsugu Hiramatsu and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, J. Physical Chem. A, 110 (13) 3738-3743 (2006).
- Vibrational Imaging of a Single Pollen Grain by Ultrabroadband Multiplex Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering Microspectroscopy. Hideaki Kano and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, Chem. Lett., 35 (10) 1124-1125 (2006).
- Molecular near-field effect and intensity enhancement of solvent modes in resonance hyper-Raman sattering. Rintaro Shimada, Hideaki Kano and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, J. Raman Spectrosc., 37, 469-471 (2006).
- Effect of water on the molecular structure and arrangement of nitrile-functionalized ionic liquids. Satyen Saha and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, J. Phys. Chem. B, 110 (6) 2777-2781 (2006).
- Dispersion-compensated supercontinuum generation for ultrabroadband multiplex coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering spectroscopy. Hideaki Kano and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, J. Raman Spectrosc., 37, 411-415 (2006).
- Three-Dimensional Vibrational Imaging of a Microcrystalline J-Aggregate Using Supercontinuum-Based Ultra-Broadband Multiplex Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering Microscopy. Hideaki Kano and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, J. Phys. Chem. B, 110 3120-3126 (2006).
- Hyper-Raman microspectroscopy: a new approach to completing vibrational spectral and imaging information under a microscope. Rintaro Shimada, Hideaki Kano and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, Optics Lett., 31 (3) 320-322 (2006).
- A new nonlinear Raman probe for local structures in liquids and solutions. Shinsuke Shigeto and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, Chem. Phys. Lett., 417, 149-153 (2006).
- A new class of magnetic fluids: bmim[FeCl4] and nbmim[FeCl4] ionic liquids. Satoshi Hayashi, Satyen Saha and Hiro-o Hamaguchi, IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 42, 12-14 (2006).
総説・解説
- イオン液体のナノ構造と特異性. 奥野将成, 濵口宏夫 「ナノ学会会報」 5 (1) 9-12 (2006).
- 磁性イオン液体:磁石にくっつく不思議な液体. 奥野将成, 濵口宏夫 「サイエンスネット」 27, 14-15 (2006).
- ラマン分光で見る分子レベルでの生命活性 -細胞物理化学事始め-. 内藤康彰, 黄郁珊, 濵口宏夫 Biophilia 2 (3) 14 (2006).
- 単一酵母生細胞のIn Vivoラマン分光/イメージングと生命のラマン分光指標. 黄郁珊, 内藤康彰, 加納英明, 濵口宏夫 「化学と生物」 44, 8, 551-555 (2006).
- 非線形ラマン顕微分光法による振動分光イメージング―分子性結晶から単一生細胞まで―. 加納英明, 島田林太郎, 濵口宏夫 「応用物理」 75, 6, 682-688 (2006).
- 酵母単一生細胞の時空間分解ラマン分光. 黄郁珊, 濵口宏夫 「蛋白質 核酸 酵素」 51, 3, 262-267 (2006).