
Time-Resolved Infrared Spectroscopic System (mid wavelength IR) (4000-800cm-1)
Nanosecond Time-resolved Infrared Spectrometer
Nanosecond to microsecond dynamics of photo-excited molecules are detected as temporal changes in infrared absorption spectra. The sensitivity of the system is so high that very small changes in absorbance (ΔA=10-6) can be detected.
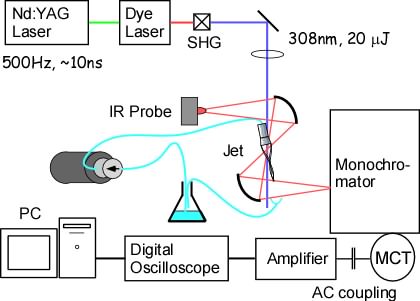
Fig. 1. Setup
Molecules are photo-excited by the second harmonic of the output of a Nd:YAG laser pumped dye laser (Fig. 2). The pump laser beamd is overlaped with the infrared probe beam on the sample jet (Fig. 3).

Fig. 2. Nd:YAG laser & Dye laser

Fig. 3. Sample Jet
The infrared probe light is dispersed by a monochromator and detected by an MCT detector (Fig. 4).

Fig. 4. Spectrometer & Detector
Reverse Proton Transfer Reaction in the Ground State of 2-aminopyridine with Acetic Acid Complex
Stepwise double proton transfer takes place in the electronic excited state of 2-aminopyridine-acetic acid complex (Ref. [1]). The reverse proton transfer reaction is observed as the recovery of the bleaching of NH bending band (Fig. 7,8).
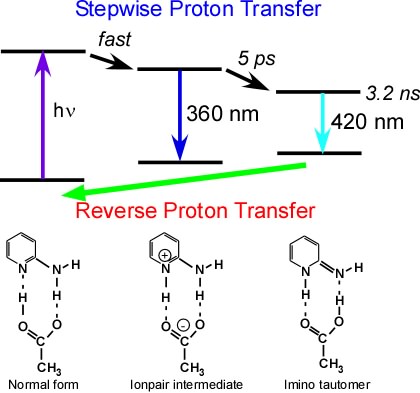
Fig. 5. Proton transfer reactions of 2-amnopyridine-acetic acid complex
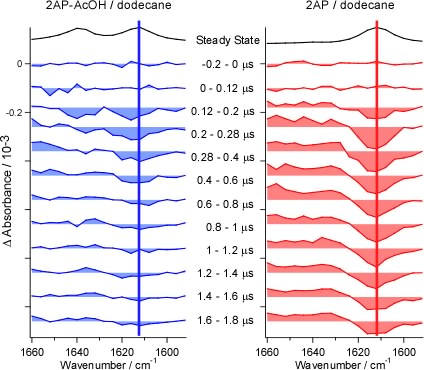
Fig. 6. Time-resolved infrared difference spectra
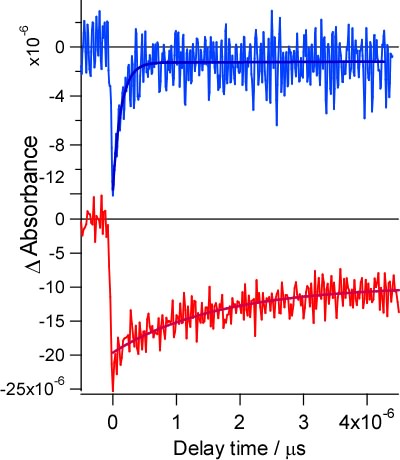
Fig. 7. Temporal change in the infrared absorption at 1640cm-1 2-aminopyridine-acetic acid (blue line), 2-aminopyridine monomer (red line)
References
- H. Ishikawa, K. Iwata and H. Hamaguchi, J. Phys. Chem., 106, 2305, (2002).
- S. Sato, C. Kudo and H. Hamaguchi, proceedings for twelfth Time -Resolved Vibrational Spectroscopy Conference