
785nm Near-Infrared-Excited Raman Microspectroscopic System
Near-Infrared-Excited Raman Microspectroscopy
- Raman Microspectroscopy
- Vibrational spectra reflect molecular structures
suitable for in vivo measurement
sub-µm spacial resolution
disadvantage: interference from fluorescence → Near-infrared excitation enables us to eliminate the interference from fluorescence - Molecular labeling for protein detection
- By using a label molecule, which has large NIR Raman scattering cross section, sensitivity of Raman detection is improved. (Fig. 1)
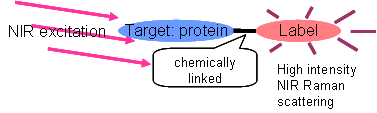
Fig. 1. Molecular labeling
Experimental Set-Up
By using a Ti:Sapphire laser, high laser power and wavelength tunability become available.

Fig. 2. Apparatus
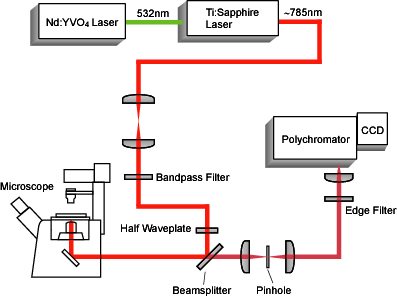
Fig. 3. Setup
Molecular Labeling
Dabsyl (Fig.4) labeling increases the detection sensitivity of bovine serum albumin (BSA) by a factor of ten. Raman mapping shows good contrast image of BSA location by using the BSA labeling. (Fig. 5)
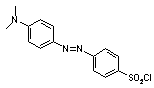
Fig. 4. Label molecule: dabsyl chloride
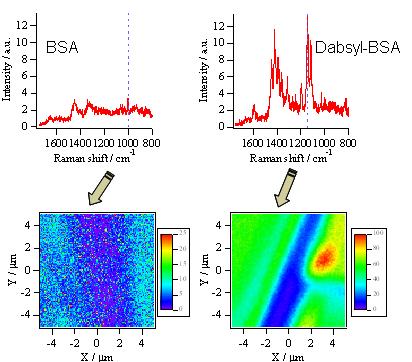
Fig. 5. Raman mapping image